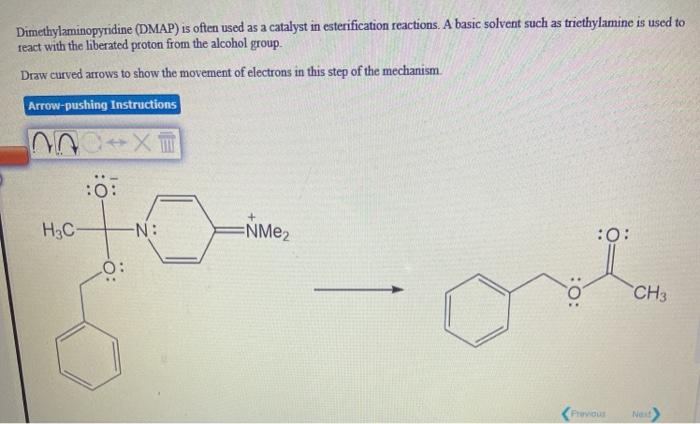
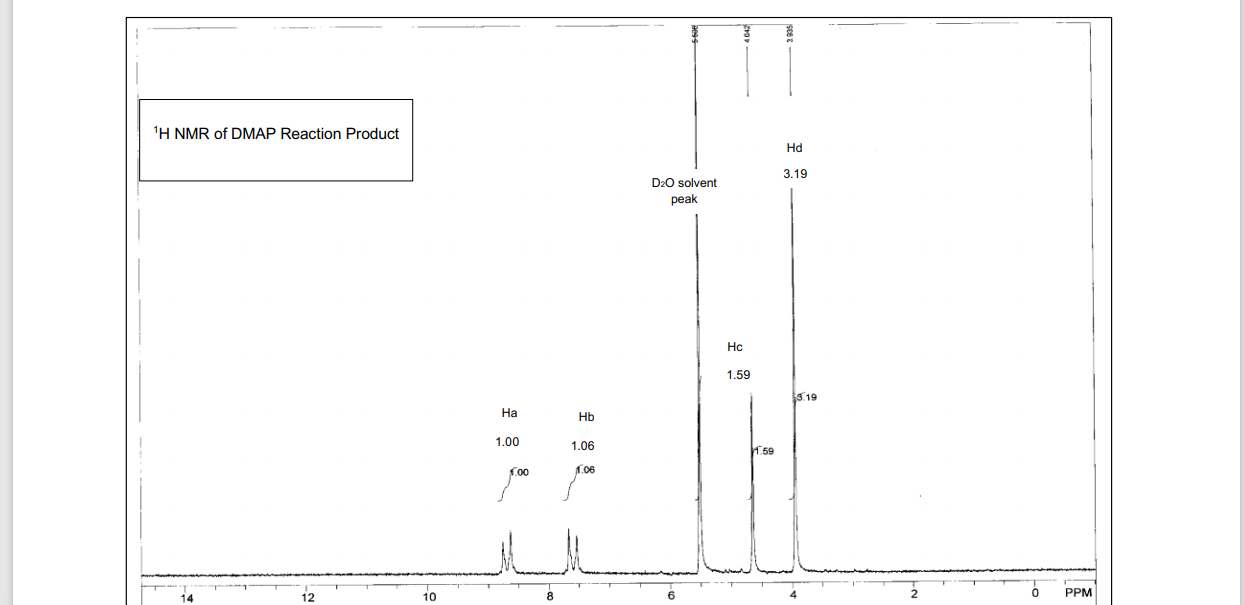
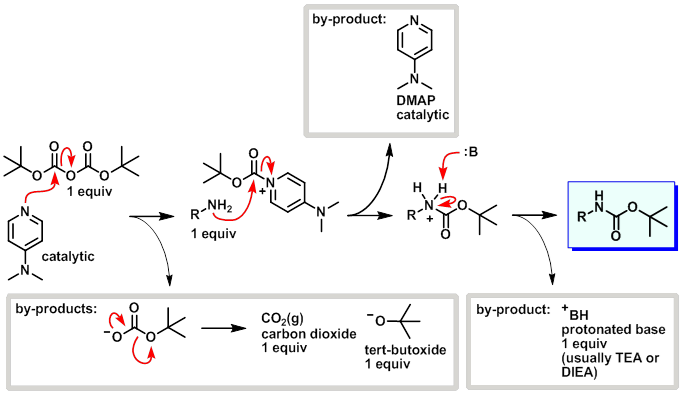
Dmap Reaction. Mechanism of the Yamaguchi Esterification Addition of the carboxylate to the carboxylic acid chloride forms the mixed anhydride: DMAP is an acyl transfer reagent that reacts regioselectively at the less hindered carbonyl site: DMAP is a stronger nucleophile than the alcohol. First, DMAP and acetic anhydride react in a pre-equilibrium reaction to form an ion pair of acetate and the acetylpyridinium ion. The reaction mechanism has also been studied experimentally in dichloromethane through analysis of the reaction kinetics for the acetylation of cyclohexanol with acetic anhydride, in the presence of DMAP as catalyst and triethylamine as the auxiliary base. This intermediate cannot form intramolecular side products but reacts rapidly with alcohols. The reaction mechanism is described as follows: With amines, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding amides because amines are more nucleophilic. Notably, compared with common organic tosylation with a low dose of DMAP. DMAP accelerates the reaction rate by reacting with the O -acylisourea intermediate to form a highly activated electrophilic acylated pyridinium intermediate. DMAP, an activating reagent, was used to facilitate the reaction, owing to the similarities of sulfonyl and acyl transfer.

Dmap Reaction. This intermediate cannot form intramolecular side products but reacts rapidly with alcohols. Reaction of this ion pair with the alcohol substrate yields the final product, tert-butylacetate. Mechanism of the Yamaguchi Esterification Addition of the carboxylate to the carboxylic acid chloride forms the mixed anhydride: DMAP is an acyl transfer reagent that reacts regioselectively at the less hindered carbonyl site: DMAP is a stronger nucleophile than the alcohol. DMAP, an activating reagent, was used to facilitate the reaction, owing to the similarities of sulfonyl and acyl transfer. The competing base-catalyzed reaction pathway can either. Dmap Reaction.
The reaction mechanism is described as follows: With amines, the reaction proceeds without problems to the corresponding amides because amines are more nucleophilic.
You can also try to quench your reaction with dilute.
Dmap Reaction. Notably, compared with common organic tosylation with a low dose of DMAP. Development of new DMAP-related organocatalysts for use in the Michael addition reaction of β-ketoesters in water. Quench the RM with respective qty of water than add solvent to extract the compound. This intermediate cannot form intramolecular side products but reacts rapidly with alcohols. DMAP is a very effective acyl transfer agent.
Dmap Reaction.